What is Access Control?

What is Access Control?
Access Control is a system that helps control access rights to data to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing an organization's internal resources. It specifies who is allowed to perform any actions within the organization's network or premises and can also determine which resources those individuals are allowed to access. Additionally, it serves as a tool to monitor entry and exit times since Access Control systems keep accurate time records as evidence. This enhances the security of personnel and assets within the organization.
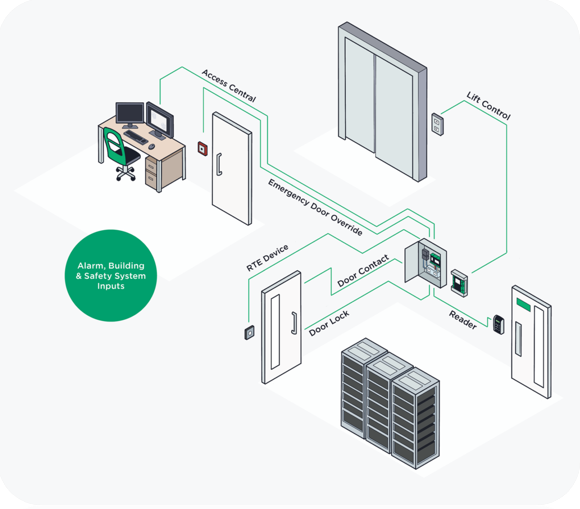
typically include card scanners, keycard scanners, or card swipe machines. Keycard scanners are commonly used in conjunction with keycards. The card scanner is often mounted on the outside of the door and consists of various components, including:
- Control box (Power Supply): Controls entry and exit, positioned above the door. It is equipped with a battery for backup power in case of a power failure.
- Magnetic Lock: Attached to the door frame and door leaf, this lock secures the door. Without proper authorization, the door cannot be opened.
- Exit Switch: A button located on the inside of the door for exiting the premises.
- Additional devices: Such as a remote control for authorized personnel, an Emergency Key switch for situations where the door is left open or the lock system is compromised, a Door Bell, and an Alarm Bell.
Example 1
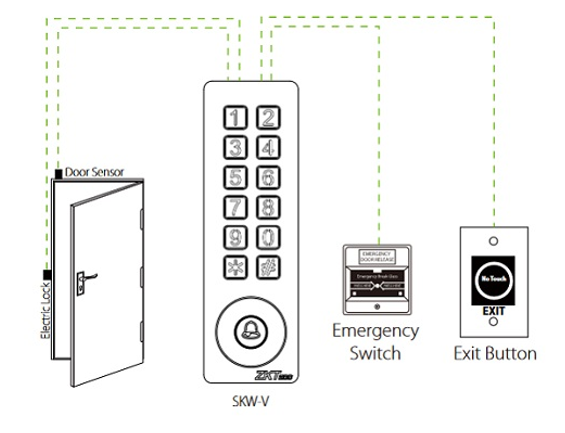 Example 2
Example 2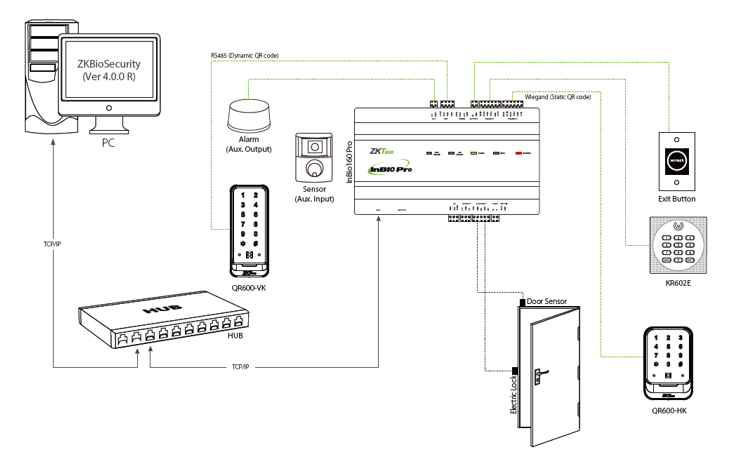
2. Access Control systems that utilize the human body as confirmation
Biometric authentication systems, whether fingerprint or facial recognition, provide a higher level of security as they are unique to each individual, making replication or borrowing impossible, unlike keycards. Users benefit from maximum convenience.
- Fingerprint Scanner or Finger Scan: Operates similarly to card scanners or card swipe machines, but the verification device is replaced with the user's fingerprint.
- Face Scan Security System: The face scanning system functions similarly to other access control systems but uses the user's face as the means of identification instead of fingerprints or keycards. This enhances the security efficiency of the system.
Example 1
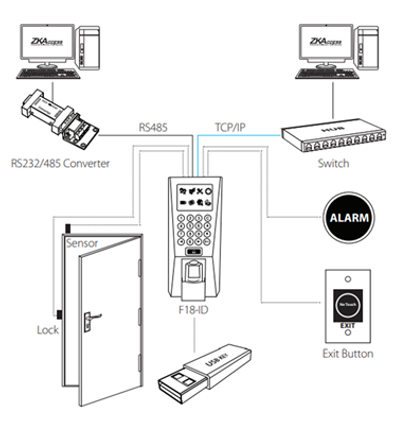
Example 2
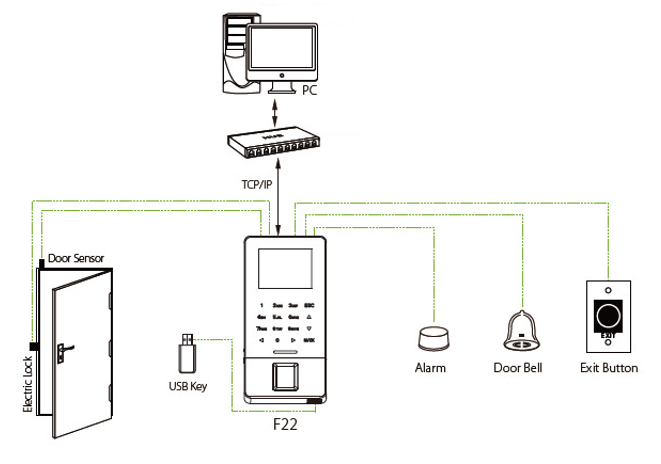
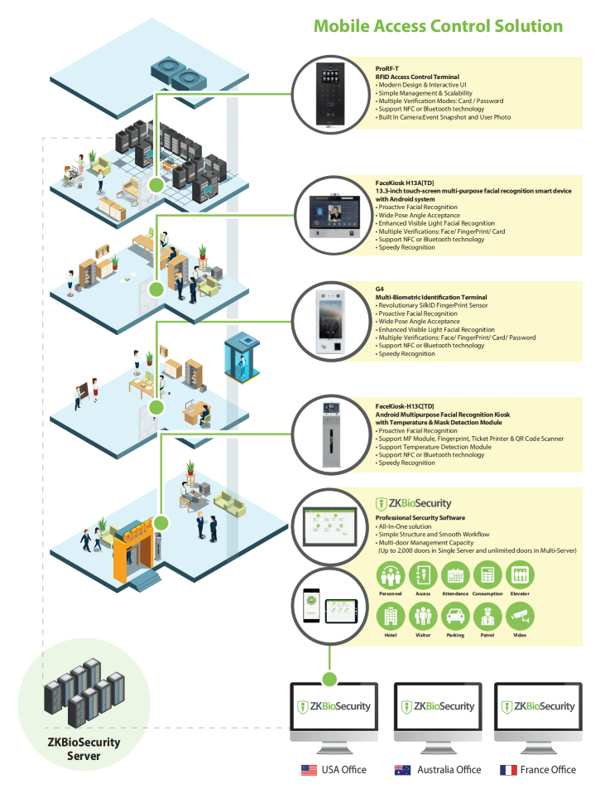
Mobile Access Control refers to the authentication of identity using mobile devices, typically smartphones, as a replacement for traditional key cards when entering or exiting buildings or important locations. Smartphones are convenient for carrying and contribute to increased security by allowing the storage of user data for identity verification purposes.